Horsepower to Amps Calculator
Calculate current (Amps) from power (Horsepower), voltage, and efficiency for both AC and DC circuits.

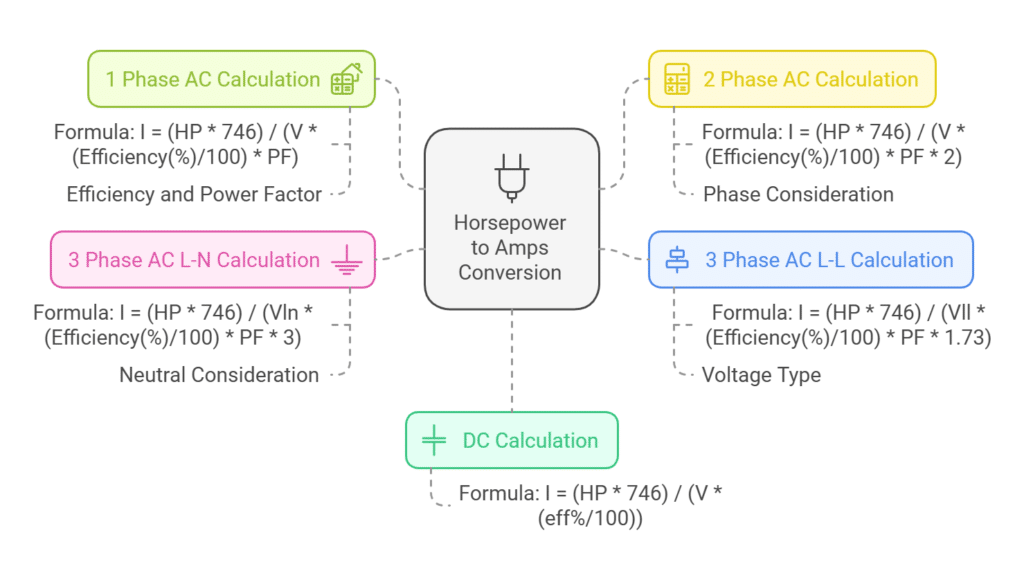
Horsepower to Amps Conversion
To convert horsepower (hp) to amps, you need to know the voltage (V) and, for AC systems, the power factor (PF) and efficiency (Eff), because horsepower measures power while amps measure current. The conversion depends on whether it’s a DC or AC system (single-phase or three-phase).
Basics
Horsepower (HP)
A unit of power measuring the rate of energy usage. One horsepower equals 746 watts.
Ampere (A)
A unit of electric current measuring the rate of electric charge flow. One ampere equals one coulomb per second.
Conversion Formulas
Choose the appropriate formula based on your circuit type
Line to Line:
I(A) = (HP × 746) / (Vll × (Efficiency(%) / 100) × PF × 1.73)Line to Neutral:
I(A) = (HP × 746) / (Vln × (Efficiency(%) / 100) × PF × 3)Practical Examples
Step-by-step calculations for different scenarios
DC Motor Example
BasicProblem: Calculate the current for a 5 HP DC motor with:
- Voltage: 240V
- Efficiency: 85%
Solution:
- Use formula: I = (HP × 746) / (V × (Efficiency/100))
- Insert values: I = (5 × 746) / (240 × (85/100))
- Calculate: I = 18.3 Amps
Typical Power Factor Values
| Device | Typical Power Factor |
|---|---|
| Resistive Load | 1.0 |
| Fluorescent Lamp | 0.95 |
| Incandescent Lamp | 1.0 |
| Induction Motor (Full Load) | 0.85 |
| Induction Motor (No Load) | 0.35 |
| Synchronous Motor | 0.90 |
Common HP to Amps Conversions (240V, 85% Efficiency)
| Horsepower (HP) | DC Circuit (A) | Single Phase AC (PF=0.9) | Three Phase AC (PF=0.9) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.2 |
| 1.0 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 2.3 |
| 2.0 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 4.7 |
| 3.0 | 11.0 | 12.2 | 7.0 |
| 5.0 | 18.3 | 20.3 | 11.7 |
| 7.5 | 27.4 | 30.5 | 17.6 |
| 10.0 | 36.6 | 40.6 | 23.4 |
| 15.0 | 54.9 | 61.0 | 35.2 |
| 20.0 | 73.2 | 81.3 | 46.9 |
| 25.0 | 91.5 | 101.6 | 58.7 |
Note: Values are rounded to one decimal place. Actual current may vary based on specific motor characteristics and operating conditions.