Ohm’s Law Calculator
Please provide any 2 values and click “Calculate” to get the other values in the ohm’s law equations V = I × R and P = V × I.
What is Ohm’s Law
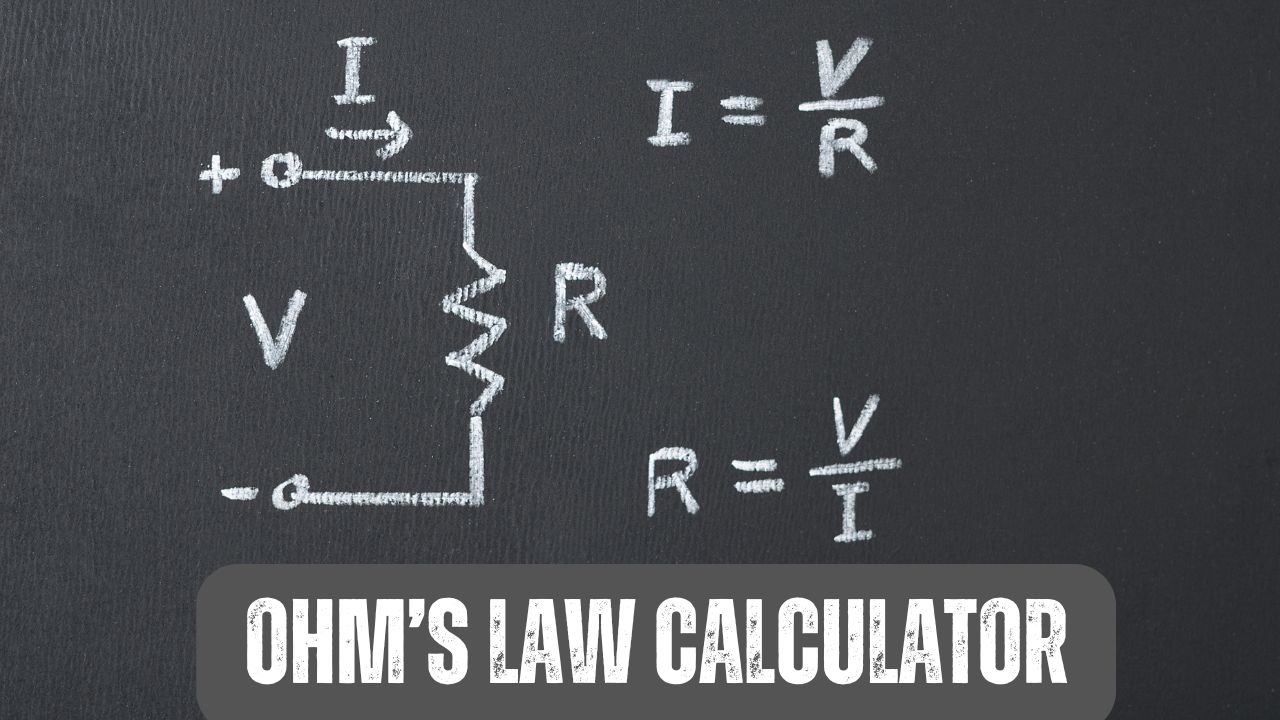
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electronics and physics that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
It states that the voltage (V) across a conductor is equal to the product of the current (I) flowing through it and the conductor’s resistance (R).
Mathematically, it is expressed as
V = I * R
Where:
- Voltage (V): The electrical pressure that drives current through a circuit. Think of it as the force pushing electrons. It is measured in Volts (V).
- Current (I): The flow of electrical charge, or electrons, through a circuit. It is measured in Amperes (A or Amps).
- Resistance (R) opposes the current flow in a circuit and limits it. It is measured in Ohms (Ω).
Ohm’s Law Equation
Ohm’s law states the relationship between electric current and potential difference. The current flowing through most conductors is directly proportional to the voltage. Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist, proved Ohm’s law experimentally.
V = IR,
There are many ways to use it:
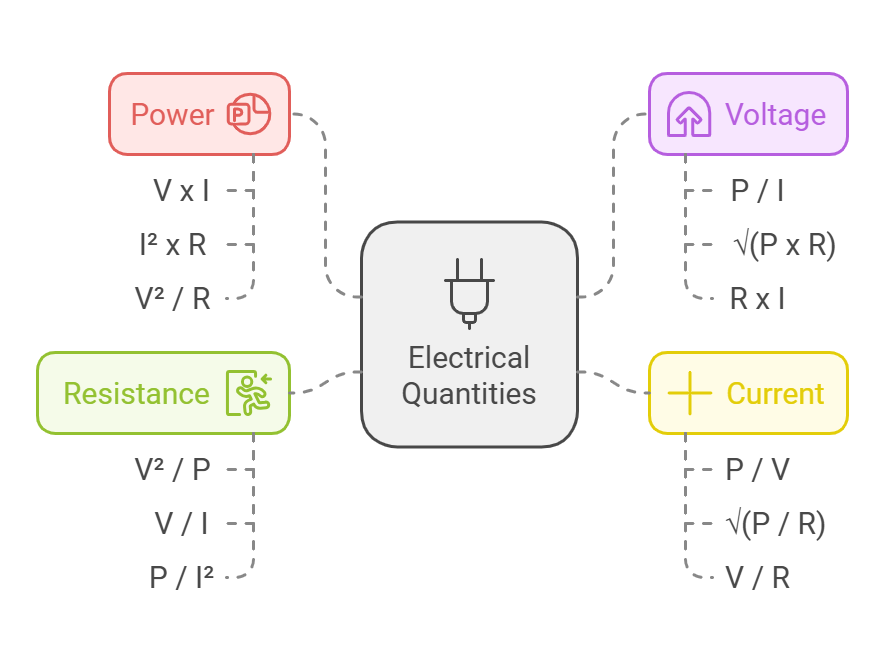
Quadrant 1: Power (watts)
Power is the rate at which energy is used or produced.
- V x I (Voltage times Current)
- I² x R (Current squared times Resistance)
- V² / R (Voltage squared divided by Resistance)
Quadrant 2: Voltage (volts)
Voltage is the electrical “pressure” that pushes current through a circuit.
- P / I (Power divided by Current)
- √(P x R) (Square root of Power times Resistance)
- R x I (Resistance times Current)
Quadrant 3: Current (amps)
Current is the flow of electrical charge through a circuit.
- P / V (Power divided by Voltage)
- √(P / R) (Square root of Power divided by Resistance)
- V / R (Voltage divided by Resistance)
Quadrant 4: Resistance (ohms)
Resistance is the opposition to current flow in a circuit.
- V² / P (Voltage squared divided by Power)
- V / I (Voltage divided by Current)
- P / I² (Power divided by Current squared)
