Amps to Horsepower Calculator
Calculate power (Horsepower) from current (Amps), voltage, and efficiency for both AC and DC circuits.
- Amps to Horsepower Conversion
- Ampere (A)
- Horsepower (HP)
- Conversion Formulas
- DC Circuit Calculation
- AC Single Phase Calculation
- AC Two Phase Calculation
- AC Three Phase Calculation
- Typical Power Factor Values
- FAQs
- What is the difference between Amps and Horsepower?
- How do I convert Amps to Horsepower?
- What is a Power Factor?
- Why is the Power Factor important?
- Related Tools
- Reference
- Author
Amps to Horsepower Conversion
The conversion from Amperes (A) to Horsepower (HP) depends on voltage and system type (DC, single-phase AC, or three-phase AC).
Ampere (A)
A unit of electric current measuring the rate of electric charge flow. One ampere equals one coulomb per second.
Horsepower (HP)
A unit of power measuring the rate of energy usage. One horsepower equals 746 watts.
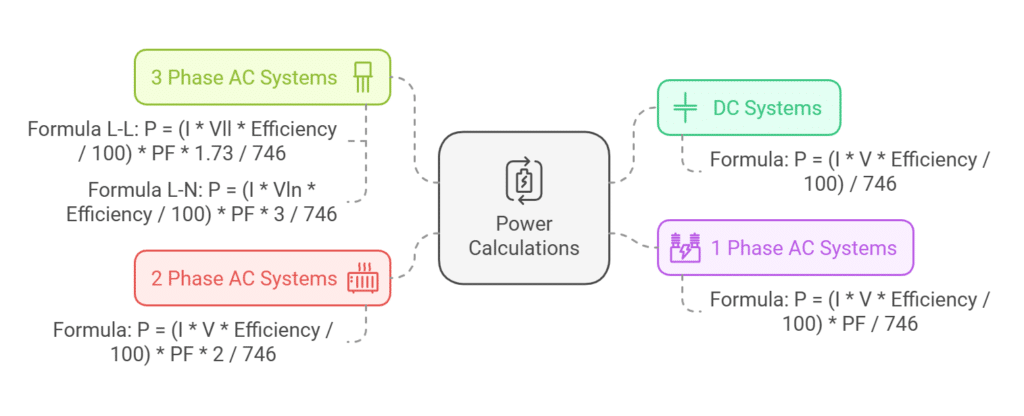
Conversion Formulas
DC Circuit Calculation
Where:
- P = Power in Horsepower
- I = Current in Amps
- V = Voltage in Volts
- Efficiency = Efficiency percentage
AC Single Phase Calculation
Where:
- PF = Power Factor
- I = Current in Amps
- V = RMS Voltage in Volts
- Efficiency = Efficiency percentage
AC Two Phase Calculation
AC Three Phase Calculation
Line to Line:
P(HP) = (I(A) × Vll(V) × (Efficiency(%) / 100) × PF × 1.73) / 746Line to Neutral:
P(HP) = (I(A) × Vln(V) × (Efficiency(%) / 100) × PF × 3) / 746Typical Power Factor Values
| Device | Typical Power Factor |
|---|---|
| Resistive Load | 1.0 |
| Fluorescent Lamp | 0.95 |
| Incandescent Lamp | 1.0 |
| Induction Motor (Full Load) | 0.85 |
| Induction Motor (No Load) | 0.35 |
| Synchronous Motor | 0.90 |
Important: These are typical values. For accurate calculations, use the actual power factor of your device.
FAQs
What is the difference between Amps and Horsepower?
Amps measure the flow of electric current, while Horsepower measures the rate of energy usage. The relationship between them is defined by the voltage, efficiency, and power factor in the circuit.
How do I convert Amps to Horsepower?
To convert Amps to Horsepower, use the appropriate formula for your circuit type (DC or AC). You need to know the voltage, efficiency, and power factor to perform this calculation.
What is a Power Factor?
The Power Factor (PF) is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being converted into useful work output. It is the ratio of real power (Watts) to apparent power (Volt-Amps).
Why is the Power Factor important?
A low power factor indicates poor efficiency, which can lead to higher energy costs and potential penalties from utility companies.